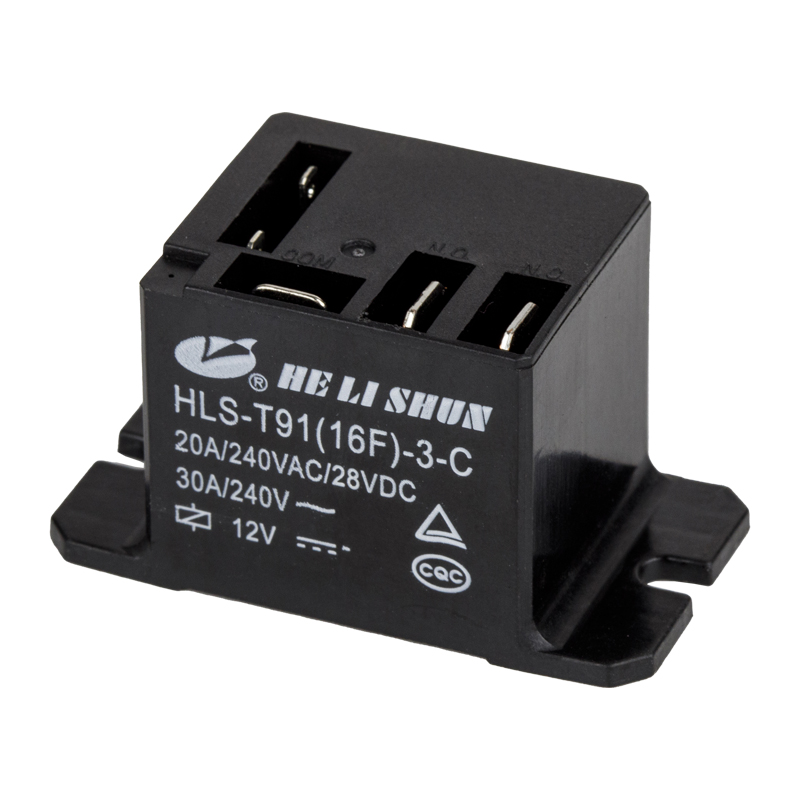
In modern automotive electrical systems, automotive relays are essentially electronic switches that allow low-current circuits (such as signals from switches or the vehicle's computer) to control high-current circuits (such as headlights, fuel pumps, or horns).
Content
Protecting Low-Current Switches and Wiring
This is the primary reason for using automotive relays. Many automotive components, such as headlights, fog lights, starter motors, or heating elements, require significant current to function properly. If these high-current loads were directly controlled by standard ignition switches or dashboard switches, the switch contacts and associated wiring would quickly burn out or overheat due to excessive current, leading to malfunctions or even fires.
Benefits of Using Relays: Relays use a small current (a low-current control signal) to activate their internal electromagnetic coil, thereby closing or opening their main contacts. In this way, high-current loads (such as 15A or higher) only flow through the relay and the load itself, protecting expensive or inconveniently replaced control switches and delicate control wiring harnesses.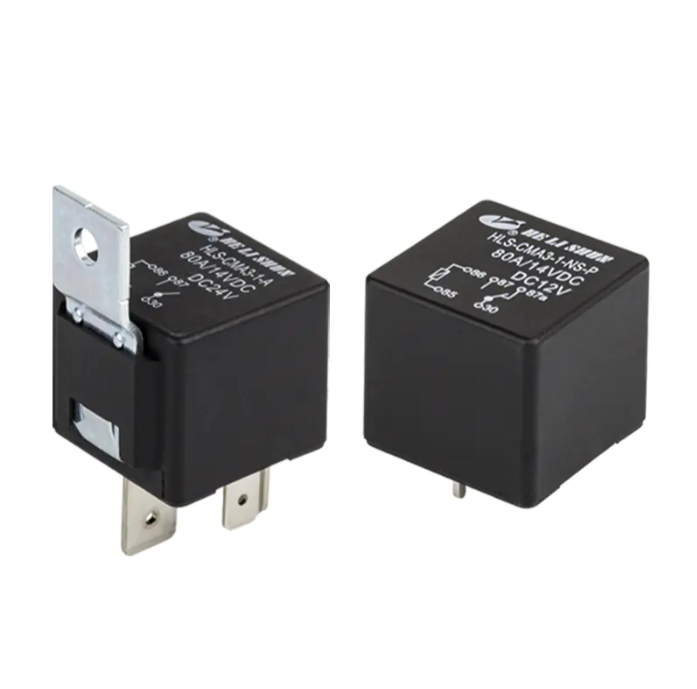
Enabling Remote Control and Automation Functions
Automotive relays are typically installed closer to high-current loads, shortening the high-current path length and reducing wiring harness resistance and power loss.
Example Applications:
- Fuel Pump Relay: Fuel pumps typically require a stable, high current. Relays can be installed close to the fuel tank, shortening wiring and ensuring efficient fuel pump operation.
- Horn Relay: Ensures the horn receives sufficient current when the switch is pressed, producing a loud and clear sound.
- Starter Motor (Starter Relay): The starter motor is one of the components in a car with the highest current demand. The use of a starter relay is crucial for ensuring reliable engine starting.
Implementing Complex Circuit Control Logic (e.g., Interlocking or Delay)
Automotive relays are also indispensable electronic components in scenarios requiring complex logic control.
Interlocking Function:
For example, in some vehicles, a function (such as power seat adjustment) can only be activated after the ignition switch is turned on and the driver is wearing a seatbelt. This can be achieved through the interlocking of multiple automotive relays.
Delay and Pulse Functions:
Some relays (such as time-delay relays) have built-in electronic circuitry to connect or disconnect circuits only after a specific time delay. Examples include the "dimming" function of interior lighting or the intermittent mode of windshield wipers.
Retrofitting and Adding High-Performance Equipment
For car modification enthusiasts, any added equipment with high current requirements should consider using automotive relays.
High-Power Lighting:
When adding LED light strips, high-performance xenon headlights (HID), or additional fog lights, they often exceed the capacity of the original wiring and switches. Using one or more automotive relays is standard and safe practice.
Audio Systems:
When installing a high-power audio system, relays may be needed to control the amplifier's power supply to ensure stable power and protect the original vehicle's electrical system.
Electric Cooling Fans:
After modifying a high-performance engine, a more powerful cooling fan may be required. These fans are typically controlled by automotive relays.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体