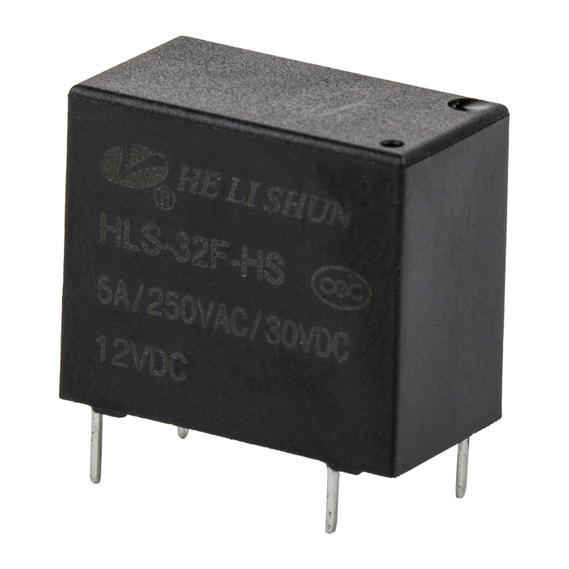
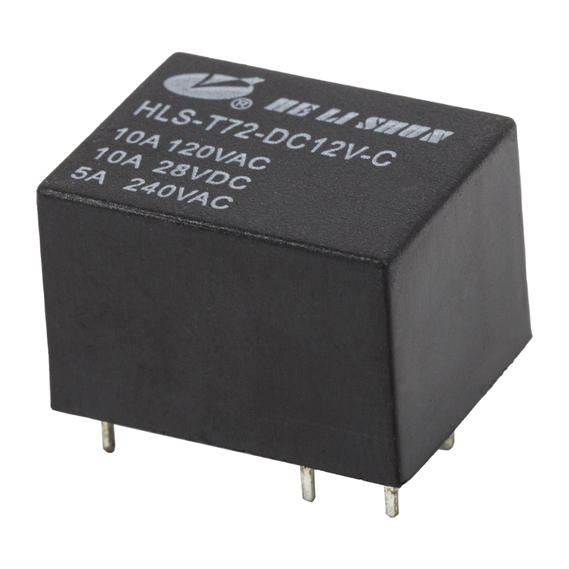
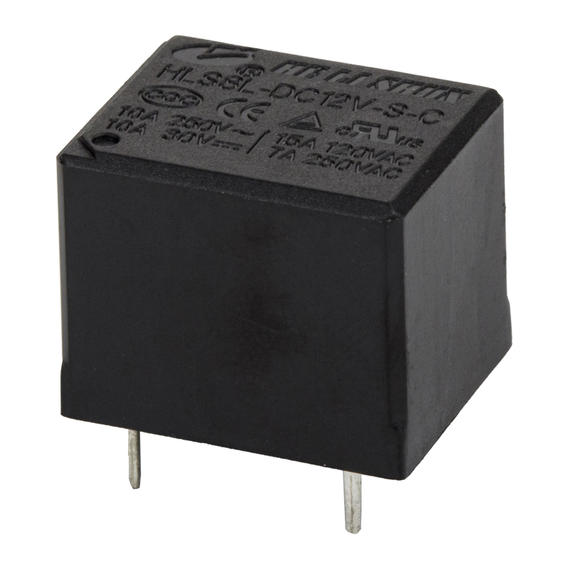
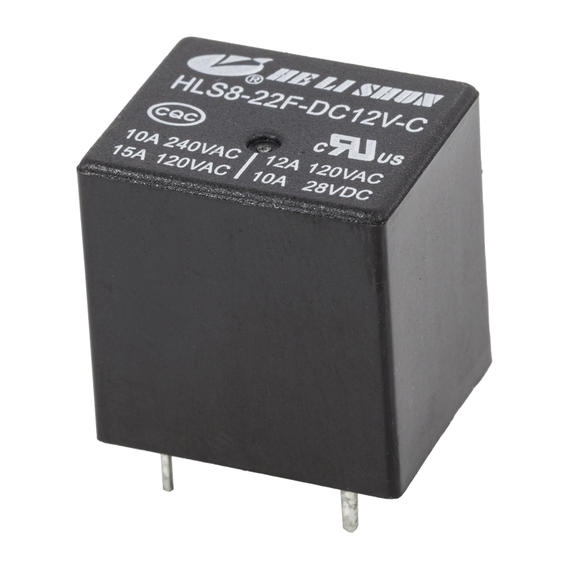
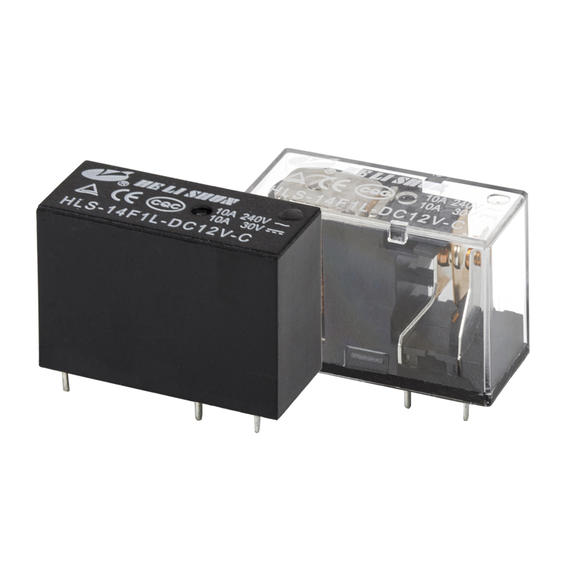
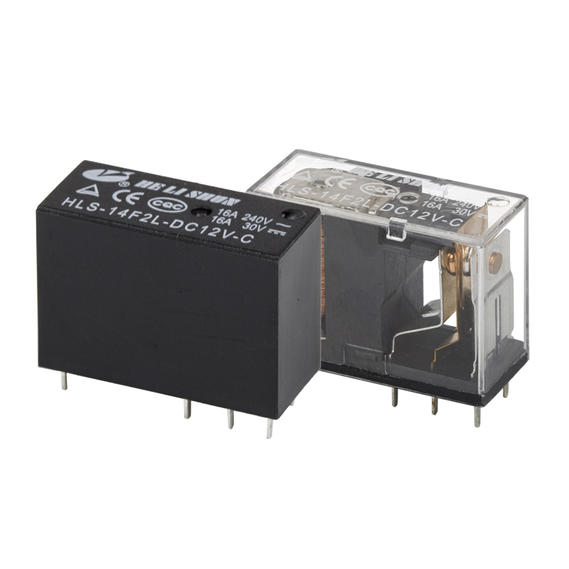
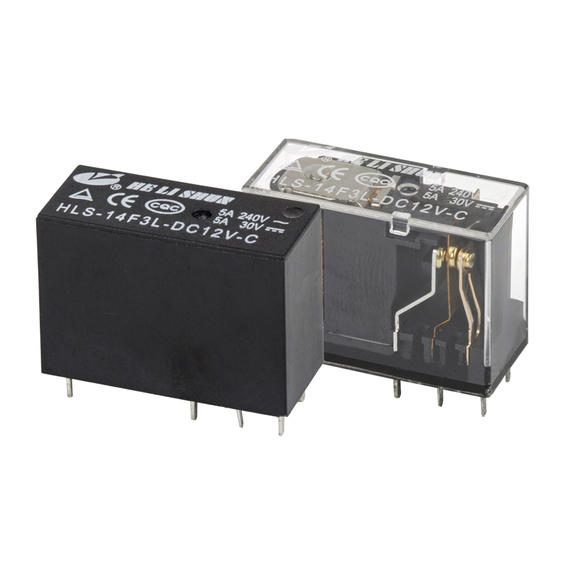
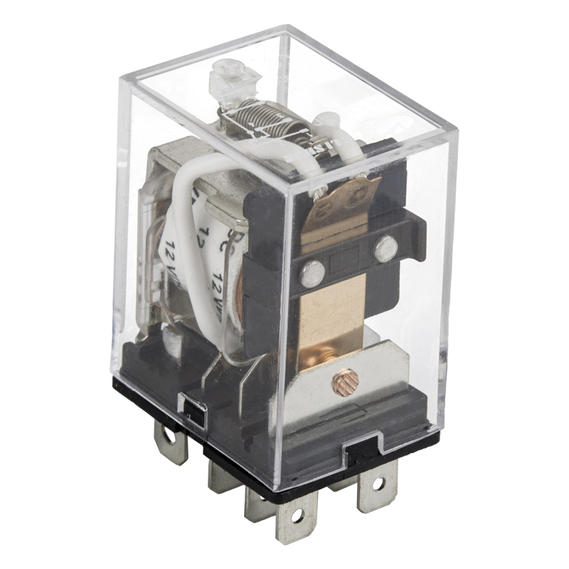
Ningbo Helishun Electron Co.,Ltd. is
founded in 2000, cover 8800 square meters. It is specialized in researching ,developing and producing
relay.
As OEM/ODM
Power Relay Manufacturers and Wholesale PCB Relay Factory, the company introduced advanced technology and had built up dependable 
quality managing system.It has passed ISO9001: 2015 quality system certification. The characteristics
and mounting layout of the products are kept accordant with foreign congeners.The company's products
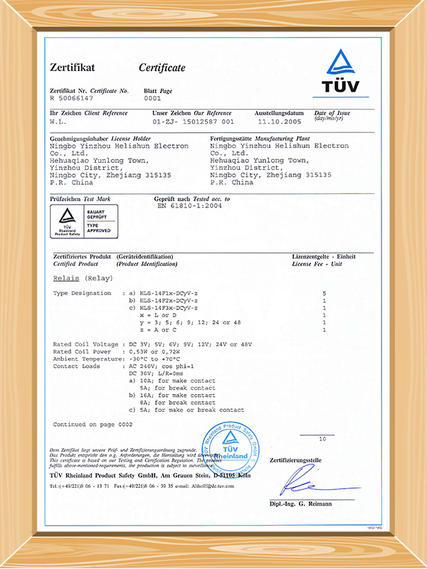
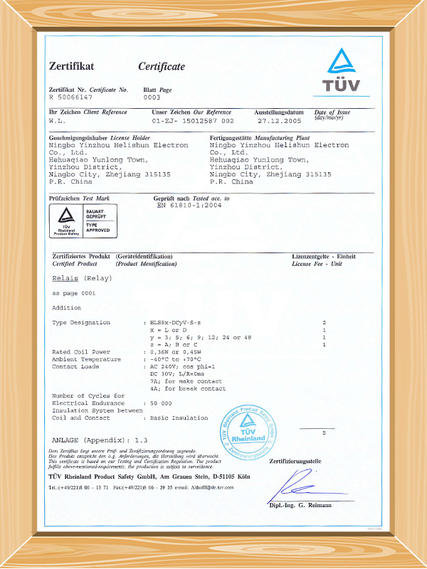
have gained the certificates of UL,TüV,CE and CQC, and comply with EU requirement of RoHS.It is a
priority to replace similar products choice. "HELISHUN" relays are well sold in home and abroad
market, and are widely used in household electrical appliance, telecommunication, automation control,
automobile, instrument and meters.Our company has many high-quality products for customers to choose from, such as HLS-4078, HLS6-23F, HLS6-4100H, etc., not only the quality can be guaranteed, but also a series of after-sales services are provided. You can contact our relevant staff.
Warmly welcome customers from home and abroad to visit our company as well as the partners of OEM and
ODM to have extensive cooperation.

Ningbo Helishun Electron Co.,Ltd.
A manufacturer specialized in manufacturing, researching and developing relays.
We show you some of our certificates we have obtained here.
The company introduces and absorbs advanced technology at home and abroad, adopts international technical quality standards, establishes a complete quality management system and testing methods, and has passed the ISO9001:2015 quality system certification.
News Center
-
 12-11-2021 Company News
12-11-2021 Company NewsWhat is the role of the relay?
The relay has the following functions:1) Expand the control range: For example, ...
Learn More
-
 12-11-2021 Company News
12-11-2021 Company NewsWhat are the uses of intermediate relays?
1. The electric shock position of the intermediate relay has the function of loa...
Learn More
-
-
Common faults of relay sockets and their solutions?
11-07-2025Common faults of relay sockets mainly include poor...
-
What role does the AC motor relay play in industrial automation?
04-07-2025In today's industrial automation and electrical co...
-
What is the environmental humidity requirement for this automotive relay?
27-06-2025The environmental humidity requirement for this au...
-
Learn More

-


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体