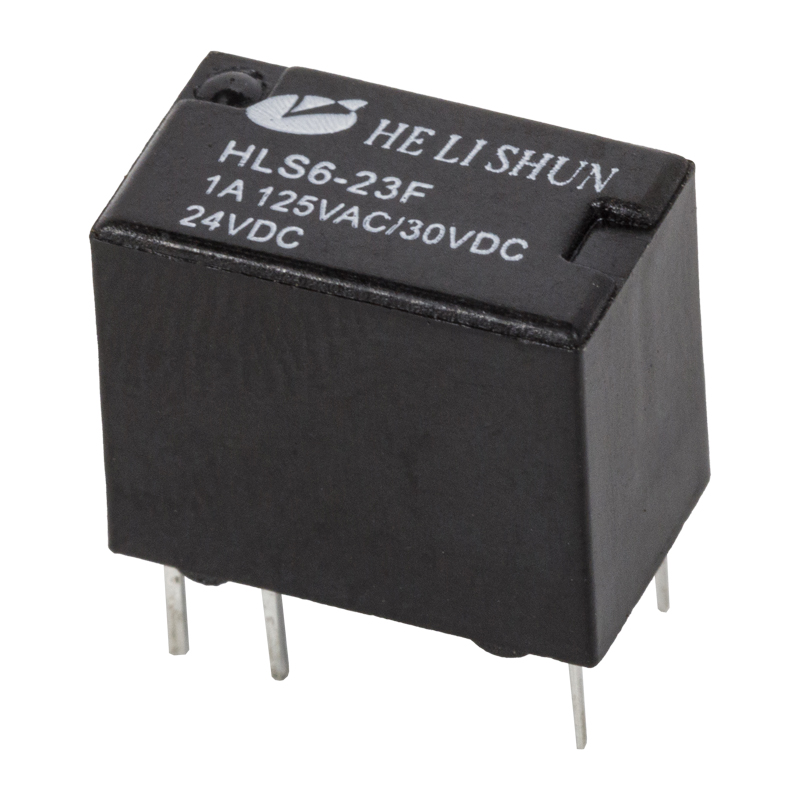
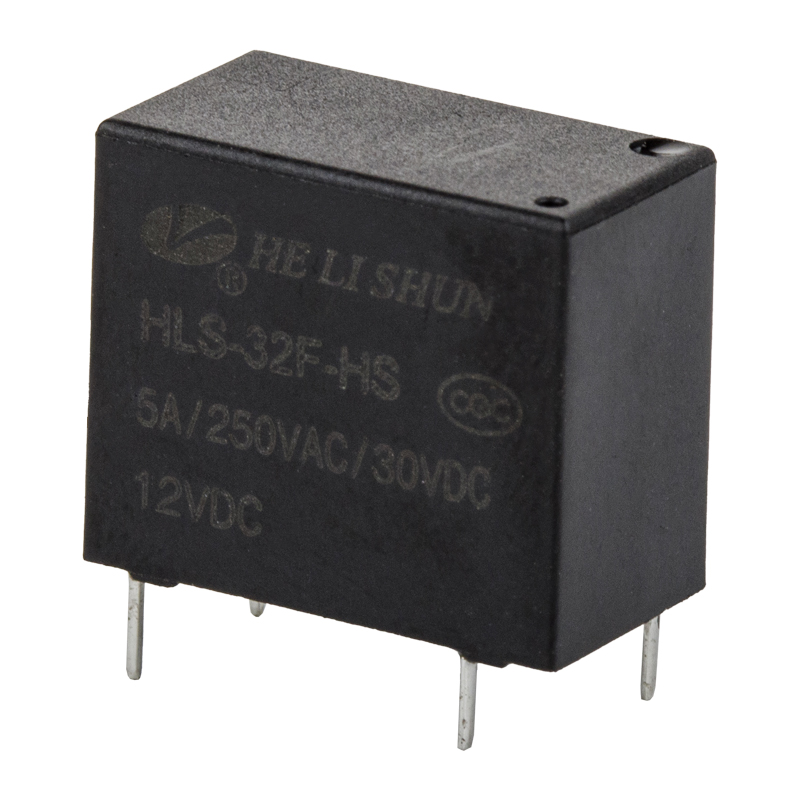
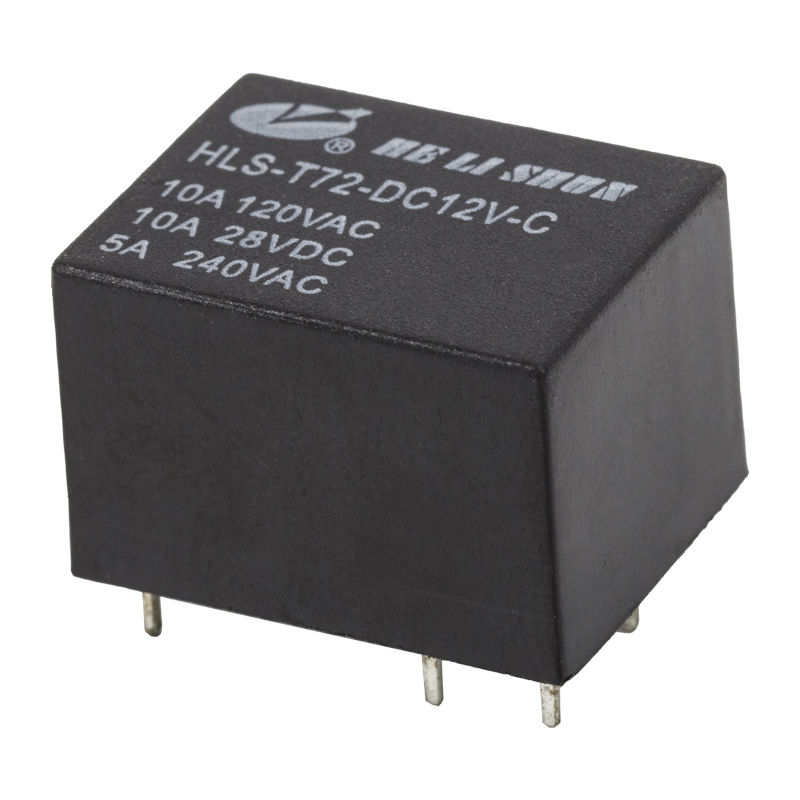
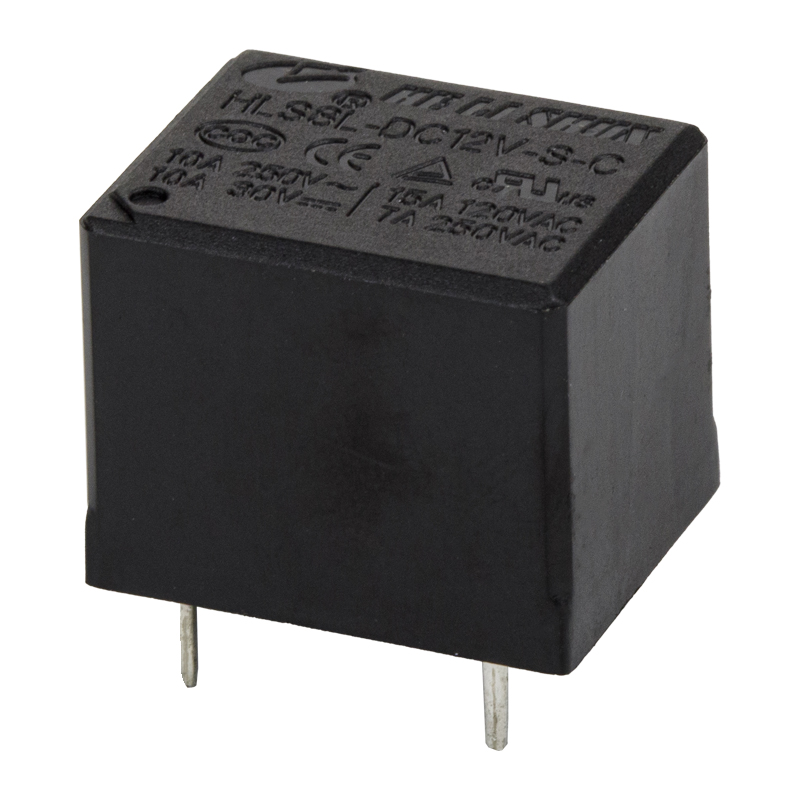
In the complex electrical systems of modern automobiles, automotive relays play a crucial role. They act as electrical "switches," allowing low-current signals (from the onboard computer or control switches) to safely control high-current circuits (such as the starter motor, headlights, fuel pump, etc.). Understanding the different types of automotive relays is not only helpful for repair and diagnosis but also key to understanding the efficient operation of automotive electrical systems.
Content
I. Standard Automotive Relays
Standard automotive relays are the most common and widely used type. They typically employ a 4-pin or 5-pin design, and their primary function is as a simple switch.
Working Principle: When the control coil is energized, it generates a magnetic field, attracting the contacts to close or open, thereby connecting or disconnecting high-current load circuits.
Main Applications: Used to control high-power devices requiring direct switching, such as headlights, fog lights, horns, wiper motors, and air conditioning compressors. They ensure that the switch in the passenger compartment only handles low current, thus extending switch life and improving safety.
II. Solid State Relays (SSRs)
Solid state automotive relays are a technology that has become increasingly popular in high-end and electric vehicles in recent years. Unlike traditional mechanical electromagnetic relays, solid state relays have no moving parts; instead, they use semiconductor elements (such as transistors or thyristors) to perform switching operations.
Working Principle: They isolate the control terminal and the load terminal through optocouplers or other electronic means, using the on and off states of semiconductor elements to control the circuit's switching on and off.
Main Applications: Due to their fast switching speed, long lifespan, lack of mechanical wear, and strong shock resistance, solid state automotive relays are ideally suited for systems requiring high control precision and response speed, such as precise control in electronic control units (ECUs), high-frequency pulse width modulation (PWM) applications, and high-voltage battery management systems in hybrid and electric vehicles.
Why are Automotive Relays Needed?
Whether you use traditional standard automotive relays or advanced solid state relays, they solve a core problem in automotive electrical systems:
- Current Isolation and Protection: Protect sensitive low-current control circuits (such as ECU outputs or driver-operated tactile switches) from high-current loads.
- Long-distance wiring optimization: Allows high-current switches to be placed closer to the load, enabling the use of shorter, thinner control wires to connect to the passenger compartment, reducing wiring harness weight and cost.
It is these ingenious automotive relays that allow us to safely and reliably start the engine, illuminate the road, and operate all onboard electronic devices with a single, small action. When troubleshooting automotive electrical systems, first checking and understanding the operation of these electromagnetic relays often yields significantly better results.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体