In today's rapidly developing information technology era, the demand for telecom relays is increasing in telecommunications equipment, test and measurement instruments, and various communication infrastructures. These special relays, often called signal relays, are key components on circuit boards, responsible for switching and transmitting low-level signals.
Content
I. Understanding the Core Characteristics of telecom relays
Before delving into relay selection criteria, we first need to understand the core differences between telecom relays and general power relays.
Low-Level Switching Capability: telecom relays are designed for switching signals at the millivolt (mV) and milliampere (mA) levels, requiring extremely low and stable contact resistance.
High-Frequency Performance: In high-speed data transmission applications, relays need excellent radio frequency (RF) performance, such as low insertion loss and high isolation.
Compact Size: Considering the increasing integration of modern electronic devices, signal relays are typically miniaturized for use on densely packed circuit boards.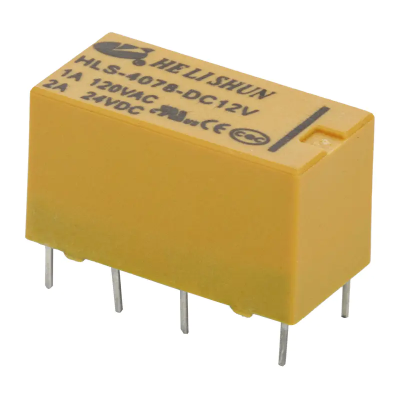
II. Key Considerations for Relay Selection
Choosing the right telecom relay requires comprehensive consideration of the following technical specifications and application requirements:
1. Technical Specifications
| Factors to consider: | Description | Impact on Relay Performance |
| Contact ratings | Maximum switchable voltage (V) and current (A). For signal relays, reliability of low-level switching is paramount. | Ensures relays do not experience contact welding or poor contact under actual operating conditions. |
| Coil power consumption | Low-power relays are the preferred choice for battery-powered or power-sensitive devices. | Reduces overall equipment energy consumption, extends battery life, and reduces heat generation. |
| Switching speed | Time required for the relay to switch from normally open to normally closed (or vice versa). Crucial for high-speed testing applications. | Affects testing efficiency and system response speed. |
| Isolation/insertion loss | Key radio frequency (RF) specifications, especially for RF switching applications. | Determines signal transmission quality and crosstalk level. |
| Electrical life | Number of reliably performed switching operations, typically in the millions. | Relates to long-term equipment reliability and maintenance costs. |
2. Packaging and Mounting
SMD (Surface Mount) vs. THT (Through-Hole Mount): Signal relays currently mostly use SMD packaging to adapt to automated production. When selecting, ensure compatibility with your PCB process.
Size and Pin Spacing: Always check that the relay size meets your board space limitations.
III. Matching Application Scenarios with Relay Type
Your application scenario directly determines the type of high-performance relay you need:
Communication Equipment (e.g., switches, routers): Focus on high-density, long-life, low-power relays. Bistable (Latching) relays are typically chosen to save standby power consumption.
Test and Measurement Instruments (e.g., oscilloscopes, spectrum analyzers): Extremely focused on high-frequency performance (high isolation, low insertion loss) and high-speed switching.
Medical Equipment: Extremely high reliability and safety requirements, potentially requiring special certification and extremely low contact resistance.
IV. Summary and Best Practices
How to Choose a Telecom Relay? The answer lies in balancing performance, size, power consumption, and cost. To make the best decision, follow these steps:
Define Requirements: Determine the type of signal you need to switch (DC/RF), the maximum voltage and current, and whether low-power characteristics are required.
Review Datasheets: Carefully compare telecom relay products from different manufacturers, especially regarding electrical life and RF performance specifications.
Sample Testing: Testing in a real-world circuit board environment is the final step in verifying the correct relay selection.
Choosing the right signal relay is fundamental to ensuring the stable and reliable operation of your communication systems and test equipment. With the proper selection of a high-quality telecom relay, overall system performance and longevity can be significantly enhanced.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体